Understanding TLS Versions and Why Upgrading to TLS 1.3 Matters
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is a protocol that secures communication over a computer network. When you visit a website, TLS ensures that the data you exchange with the site is encrypted and secure, protecting it from hackers.
An important feature of your Azure Integration Services landscape.
Differences Between TLS Versions
- TLS 1.0 (1999):
- Introduction: The first version of TLS.
- Security: It improved upon its predecessor, SSL, but now has known vulnerabilities.
- Compatibility: Widely supported, but not secure by today’s standards.
- TLS 1.1 (2006):
- Improvement: Added protection against certain types of attacks and included minor security enhancements.
- Security: Better than TLS 1.0 but still considered outdated and vulnerable to modern attacks.
- TLS 1.2 (2008):
- Advanced Security: Introduced stronger encryption algorithms and better mechanisms to ensure data integrity.
- Flexibility: Improved performance and efficiency, supporting modern cryptographic methods.
- Current Standard: Widely recommended and used because of its robust security features.
- TLS 1.3 (2018):
- Enhanced Security: Further improved encryption and significantly reduced the possibility of certain types of attacks.
- Performance: Faster handshake process, meaning quicker and more efficient secure connections.
- Simplicity: Simplified protocol with fewer configuration options, reducing the risk of misconfiguration.
- Adoption: Increasingly adopted, offering the most up-to-date security features.
Why Upgrade to TLS 1.3?
- Superior Security:
- Stronger Encryption: TLS 1.3 uses the latest encryption methods, making it extremely difficult for attackers to decrypt your data.
- Protection Against Known Attacks: TLS 1.0, 1.1, and even 1.2 are vulnerable to several known attacks, which TLS 1.3 effectively mitigates.
- Forward Secrecy: Ensures that session keys are not compromised even if the server’s private key is compromised, providing stronger long-term security.
- Improved Performance:
- Faster Connections: TLS 1.3 reduces the handshake process from two round trips to one, resulting in quicker secure connections and better performance, especially on mobile devices and high-latency networks.
- Efficient Protocols: The simplified handshake and reduced latency enhance overall user experience by speeding up page load times and reducing connection overhead.
- Compliance and Future-Proofing:
- Industry Standards: Adopting TLS 1.3 ensures compliance with the latest regulatory standards and security best practices.
- Future Compatibility: Ensures your systems are up-to-date with the latest security protocols, protecting your infrastructure against future vulnerabilities and emerging threats.
- Trust and Reliability:
- User Trust: Using the latest security protocol builds trust with your users, assuring them that their data is well-protected.
- Service Compatibility: As older versions of TLS are phased out, upgrading to TLS 1.3 ensures compatibility with modern web browsers and applications, preventing service disruptions.
In Summary: Upgrading to TLS 1.3 is essential for maintaining a secure, efficient, and reliable digital presence. It provides enhanced security, improved performance, and ensures compliance with modern standards. Staying updated with the latest security protocols like TLS 1.3 is not just a technical necessity but also a step towards building a more secure and user-friendly internet.
Make sure your Azure Integration Services are enforcing the latest version acceptable for them, currently there is a mix of TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 depending on the resource type.
If I need some assistance?
We at DevUP are experts in this area, and we use our service Helium to quickly scan the whole environment and get the TLS versions per resource, we know and will let you know when new versions of TLS is released.
Reach out, and we can show you how to get this information in minutes and continuously.
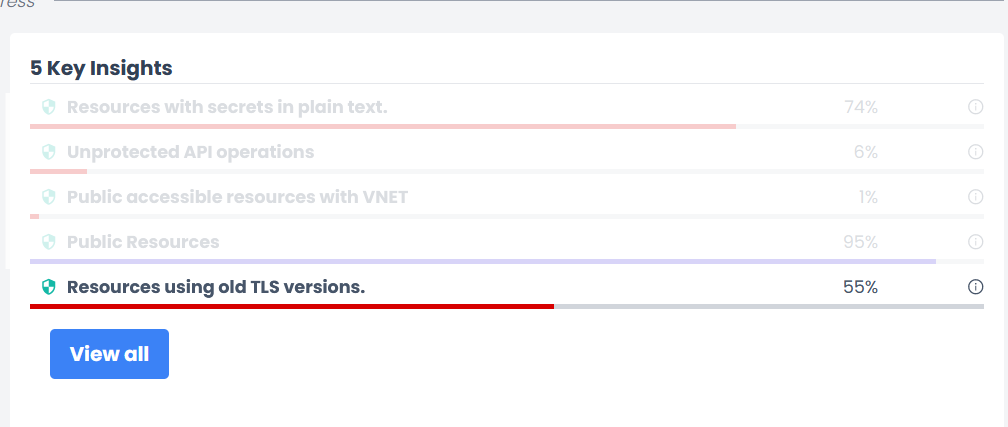 *Small sample of how you easily can track TLS settings over all your resources in Helium
*Small sample of how you easily can track TLS settings over all your resources in Helium
